Water filtration products are invaluable for bringing us clean and safe water. But have you ever considered how they’re able to do this?
There is a wide range of commercial and home water filters available today; however, they all rely on a few technologies and water purification methods to get the job done. Some filters use only one technology, while others use a combination to achieve optimum water quality.
Knowing which technology a filter uses is essential so you can determine if it will be able to effectively remove the specific contaminants or chemicals present in your water supply.
To guide you in identifying the right system for your needs, here are some of the most common water filtration technologies explained.
Activated Carbon
Activated carbon works through a process called adsorption, where chemical impurities are absorbed or trapped inside the pore structure of the carbon substrate.
Carbon filters can eliminate contaminants, such as chlorine, sediment and other volatile organic compounds, as well as unpleasant taste and odour from water. They are, however, not effective in removing nitrates, sodium and other minerals. Two types of carbon filters are available today: carbon block and granulated activated carbon.
Ceramic
One of the most inexpensive and effective water purification systems, ceramic filters have very fine pores or holes that block and remove dirt, sediments, cysts and bacteria. Ceramic filtration cannot remove chemical contaminants and undesirable odour and taste. This is why new models now come with an activated carbon core that filters most organic and metallic contaminants.
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet systems kill microorganisms by exposing them to ultraviolet light. Because UV systems are not physical filters and cannot eliminate volatile organic compounds and particulate matter, some units now come with a ceramic cartridge.
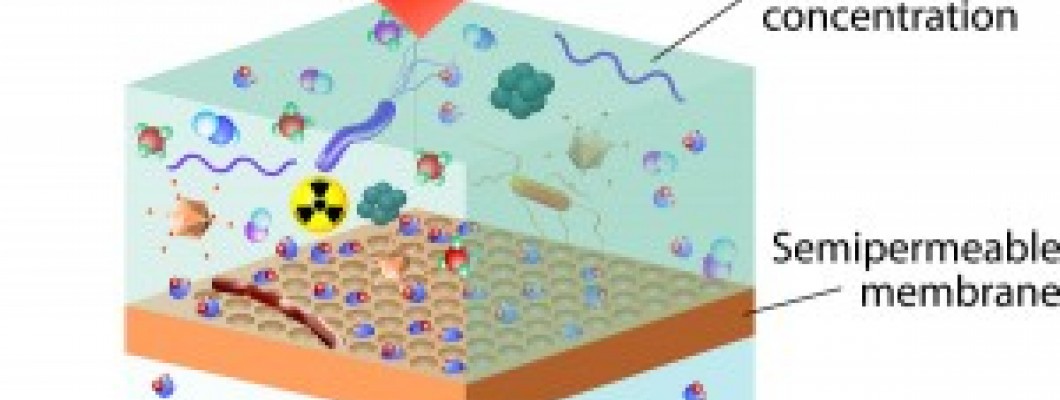
Reverse Osmosis

Pressure is applied to the contaminated water forcing water molecules through the membrane. solvent moves from a solution of greater concentration through a membrane to a solution of lesser concentration.
Reverse osmosis removes contaminants by pushing water through a very fine semi-permeable membrane, which lets water pass through but rejects insoluble particles.
Some impurities that can be eliminated by reverse osmosis filters include contaminants not removed by carbon filters, such as nitrates, arsenic and fluoride. They can also remove lead, asbestos, and other heavy metals. Many reverse osmosis water purification systems have an activated carbon filtration component, resulting in the most effective treatment against a broad range of water impurities.
One drawback to reverse osmosis filters, however, is their slow flow rates. They also produce quite a lot of waste water.
Ion Exchange
Ion exchange filters purify water by exchanging the undesirable ions, such as lead or cadmium, for the good ones, such as sodium and potassium. Softening and deionization are two of the most common ion exchange water purification methods.
While ion exchange filters effectively remove bad ions, they are not very effective when it comes to eliminating bacteria and other microorganisms. They also need to be recharged periodically with replacement ions.
Different filtration methods remove different contaminants. Knowing the strengths of weaknesses of these water filtration technologies can help you in choosing the most suitable water filtration and water purification systems for your home or office.
At Tru Water, it is our mission to provide every home or office with the right residential or commercial water filter that meets your needs. In our range, you can find the finest brands of home, office, travel and fridge filters in Australia. Call us today and let us help you find the right system.





















Leave a Comment